Notification Channels
Use Notification Channels to get notified about events across different Defender Modules, like Monitor Triggers, Workflows or Relayer Transactions lifecycle events.
Supported Channels
From Defender
- Email: Receive emails from the Defender trusted address: noreply@defender.openzeppelin.com
- Webhooks: Configure your own endpoints to receive signed notifications.
Third Party Services
Setup
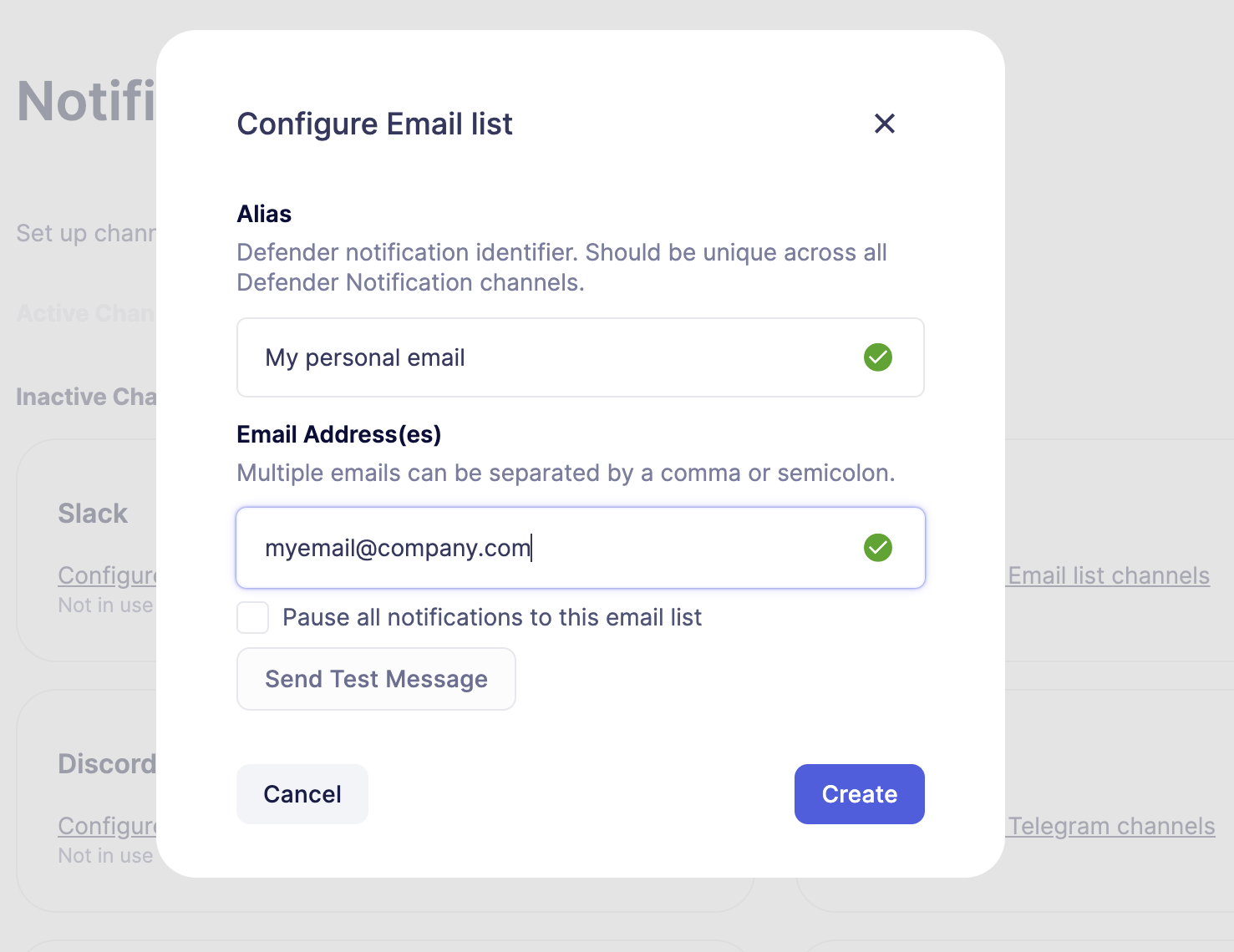
Go to Settings -> Notification Channels section and select and configure your preferred channel.
Usage
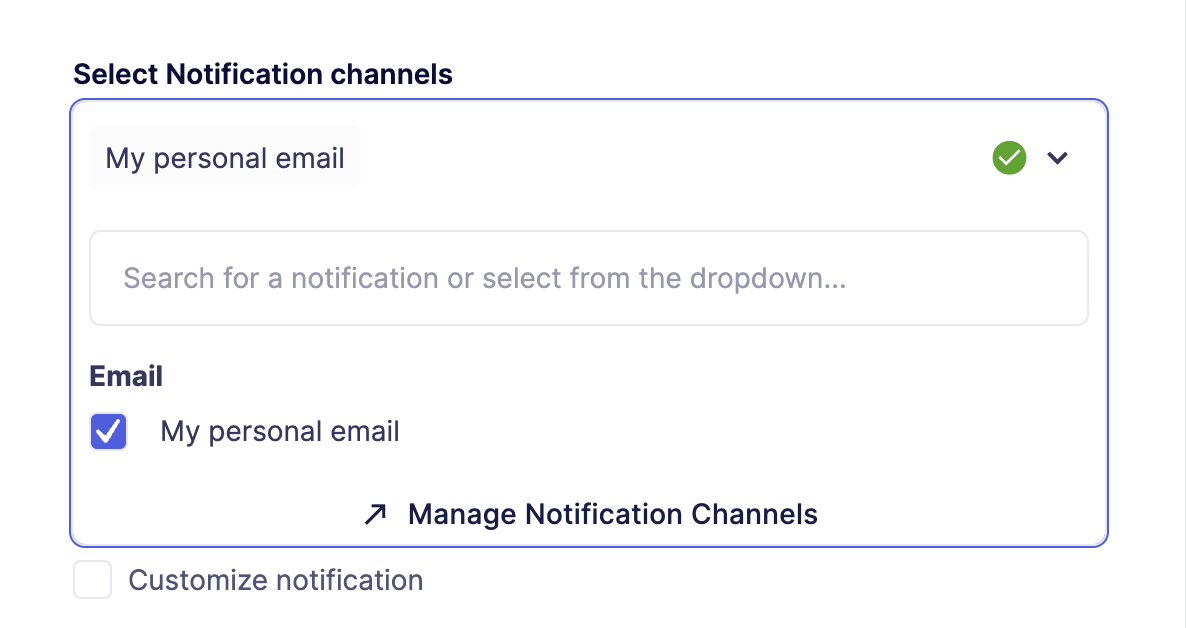
The Notification Channel can be linked to any Defender module to get notified about events.
Also, it is possible to customize the notification template, see how.
Additional configurations
Webhook Secrets
As an additional security measure, Defender implements a Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC), by adding a Defender-Signature and Defender-Timestamp request headers to the notification sent to webhook endpoints. Therefore, the endpoint receiving the notification can verify the authenticity of the request.
Each webhook notification has a secret key associated that can be accessed under Settings -> Notification Channnels -> Webhook details.
The Defender-Signature is generated using SHA256 algorithm and webhook secret to sign the payload and the timestamp.
Only Admin users in the Account have permission to see the webhook secret.
Signature Validation
Using Defender SDK
The authenticity of the signature can be validated using verifySignature utility function in Defender SDK.
function webhookHandler(req, res)
const signature = req.headers['Defender-Signature'];
const timestamp = req.headers['Defender-Timestamp'];
const defender = new Defender({
apiKey: process.env.API_KEY,
apiSecret: process.env.API_SECRET,
);
const result = client.notificationChannel.verifySignature(
body: req.body,
signature,
timestamp,
secret: process.env.WEBHOOK_SECRET,
validityInMs: 1000 * 60 * 10, // 10 mins
);
if (!result.valid) throw new Error(result.error);
// your handler code
}Manual Verification
The signature is generated using HMAC with SHA256 algorithm, so it can be verified in any programming language using the right Webhook Secret.
Python example
This code example was tested in Python 3.12. For different versions, the code might be slightly different.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, UTC
import hmac
import hashlib
def verify_signature(body_object: dict, timestamp: str, signature: str secret: str) -> bool:
# Parse the timestamp
try:
timestamp_dt = datetime.fromisoformat(timestamp)
except ValueError:
return False # Invalid timestamp format
# Get the current time and calculate the time difference
current_time = datetime.now(UTC)
time_difference = current_time - timestamp_dt
# Check if the time difference is within the allowed range (10 minutes)
if time_difference > timedelta(minutes=10):
return False
# Merge timestamp with body_object
payload_to_verify = **body_object, 'timestamp': timestamp
payload_to_verify_str = json.dumps(payload_to_verify, separators=(',', ':'))
# Create a new HMAC object using the secret and the SHA256 hash algorithm
hmac_obj = hmac.new(secret.encode(), payload_to_verify_str.encode(), hashlib.sha256)
# Generate signature
generated_signature = hmac_obj.hexdigest()
# Compare the generated signature with the provided signature
return hmac.compare_digest(generated_signature, signature)